JOURNAL OF “IRRIGATION AND MELIORATION”
 A REVIEW OF CLIMATE CHANGE IMPACTS ON WHEAT CROP IN UZBEKISTAN. M.M. Babadjanova - PhD student, Tashkent State Agrarian University
A REVIEW OF CLIMATE CHANGE IMPACTS ON WHEAT CROP IN UZBEKISTAN. M.M. Babadjanova - PhD student, Tashkent State Agrarian University
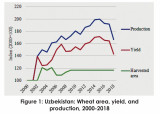
Starting from the early years of the Post-Soviet Union, wheat is considered one of the major crops in Central Asia, being a central point of many policy discussions. Wheat was the second crop occupied agricultural land which is the most important cereal crop. Recent years have witnessed growing negative climate variability that has impacted agricultural production by effecting soil fertility, water scarcity, or causing wheat diseases. The goal of this paper is to examine by reviewing the recent literature related to the impact of climate variability on wheat production in Central Asia. Different agronomic and economic methodology, also, approaches used to analyze Climate Change’s negative impacts. The review results show that there are adaptive recommendations by researchers. Agricultural policy actions are one of the main leaders to enhance adaption and mitigation. Also, continuing agricultural researches could be key for opening new doors of solutions.
Key words: Agriculture, winter wheat, productivity, climate change
28.12.2020
 HEXAVALENT CHROMIUM REMOVAL FROM AQUEOUS SOLUTION AND NATURAL ATTENUATION IN SOIL BY ADSORPTION. S.Musayev - Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, University of Connecticut, Storrs, CT, USA I.Musaev - TIIAME
HEXAVALENT CHROMIUM REMOVAL FROM AQUEOUS SOLUTION AND NATURAL ATTENUATION IN SOIL BY ADSORPTION. S.Musayev - Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, University of Connecticut, Storrs, CT, USA I.Musaev - TIIAME
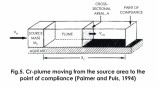
Rapid industrialization and population growth bring forward to use heavy metals in the environment and food chain. Discharge of untreated or partially treated wastewater having these toxic metals even cause more problems to water bodies and human health. Distribution of adsorbate molecules between the solid and liquid at equilibrium can be studied by adsorption isotherm models (Tella et al., 2014). Equilibrium is when concentration of adsorbate in solution is in balance with on the liquid adsorbate interface. The results show that Cr(VI) removal rate increased with adsorbent dosage till it reached equilibrium. Contact time also indicate efficiency within 60 to 70 minutes. Under certain conditions chromium hexavalent can be reduced to less toxic states in the soil by natural attenuation. Relying on this natural attenuation chromium contaminated sites can be remediated with less expense. If this method is applied, then what natural reductants are available within the aquifer should also be thoroughly studied. Reducing capacity should not prevail oxidation capacity. To study Cr (VI) reducing capacity of the aquifer by mass balances when relying on the aqueous concentrations from monitoring wells, the network must be sufficiently dense to estimate the correct Cr(VI).
Key words: Natural attenuation, food chain, heavy metals, toxic metals, adsorbent dose, adsorption isotherm, groundwater and soils.
28.12.2020
 ASSESSMENT OF WATER CONTENT IN HYDROLOGIC TIME SERIES BY USING DIFFERENCE INTEGRAL CURVES (IN THE EXAMPLE OF PSKEM RIVER). S.M.Kodirov, S.R. Mansurov Tashkent institute of Irrigation and Agricultural Mechanization Engineers, Tashkent, Uzbekistan
ASSESSMENT OF WATER CONTENT IN HYDROLOGIC TIME SERIES BY USING DIFFERENCE INTEGRAL CURVES (IN THE EXAMPLE OF PSKEM RIVER). S.M.Kodirov, S.R. Mansurov Tashkent institute of Irrigation and Agricultural Mechanization Engineers, Tashkent, Uzbekistan
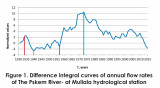
The Pskem River (mean annual flow rate 79.6 m3/s) is one of the biggest tributaries of The Chirchik River. The Chirchik River is the biggest right tributary of The Sirdarya River in the territory of Uzbekistan. On the basis of long-term data from hydrological and station (The Pskem River, at hydrological station Mullala, 85 years of observation), long-term fluctuations was evaluated in terms of watery of the year i.e. how changes mean annual flow rate from year to year. The data set of statistical characteristics and their standard errors are estimated, for average flow rates statistical error does not exceed 2.5 %, for the coefficient of variation; the error does not exceed 6 %. To describe long-term fluctuations in water content for a given period method of normalized values appied.
Key words: The Pskem River, The Chirchik River, hydrology, long-term fluctuations, average flow rate.
28.12.2020
 POSSIBILITIES OF ATTRACTING FOREIGN INVESTMENT IN THE ECONOMY OF THE REPUBLIC OF UZBEKISTAN. U.K. Akhmedov - PhD, associate professor TIIAME, S.Kh. Kholmatov - associate professor of Andijan Institute of Agriculture and Agrotechnology
POSSIBILITIES OF ATTRACTING FOREIGN INVESTMENT IN THE ECONOMY OF THE REPUBLIC OF UZBEKISTAN. U.K. Akhmedov - PhD, associate professor TIIAME, S.Kh. Kholmatov - associate professor of Andijan Institute of Agriculture and Agrotechnology
The article points out the need to attract foreign investment to the economy of Uzbekistan. Favorable conditions created for foreign investors are highlighted. Opinions are given on the solution of some of the problems that hinder the increase in investment.
Key words. Investments, foreign investors, investment climate, investment attractiveness, investment projects, centralized investments.
28.12.2020


