JOURNAL OF “IRRIGATION AND MELIORATION”
 RESEARCH OF THE ASYNCHRONOUS ELECTRIC MOTOR IN THE WINDING HEATING MODE AND IN THE DRYING MODE IN ORDER TO PREVENT ITS HUMIDITY
RESEARCH OF THE ASYNCHRONOUS ELECTRIC MOTOR IN THE WINDING HEATING MODE AND IN THE DRYING MODE IN ORDER TO PREVENT ITS HUMIDITY
M.Ibragimov - Associate Professor, D.M.Akbarov – PhD student, “Tashkent Institute of Irrigation and Agricultural
Mechanization Engineers” National Research University
Abstract: Asynchronous motors are used in many agricultural industries.Agricultural production is a production with high humidity. As noted above, one of the main reasons for the failure of electric motors in agricultural installations, during prolonged downtime, is the breakdown of insulation due to its dampness. Moistening the winding insulation will degrade the dielectric performance of the insulation. If the electric motor is often switched on and the total operating time per day is at least 4 - 6 hours in rooms with high humidity, but without ammonia vapors, then dangerous waterlogging of the windings does not occur. preheating the windings for an electric motor with a power of 3 kW, in order to maintain the state of the insulation resistance at a level safe for switching on, can be provided with a power of 12 W.
Keywords: Asynchronous motor, insulation, dampness, failure, prevention methods, dielectric, heating, temperature, humidity, motor windings.
24.03.2024
 FOREIGN EXPERIENCES ON ORGANIZATION OF AGRICULTURAL INSURANCE SYSTEM
FOREIGN EXPERIENCES ON ORGANIZATION OF AGRICULTURAL INSURANCE SYSTEM
Q.Nosurullaev – PhD student, “Tashkent Institute of Irrigation and Agricultural Mechanization Engineers” National Research University
Abstract: Insurance plays an important role as part of climate change adaptation strategies for agriculture and households in developing countries. However, there are many problems in the market that hinder the full development of agricultural insurance services in agriculture. In Uzbekistan, agriculture is reflected in such market problems as information asymmetries, high costs, poor infrastructure, and public distrust of insurance services. The government's provision of special subsidies to increase coverage and a number of other changes could lead to some market growth.
Keywords: agricultural risk insurance, insurance premiums, insurance services, climate change, insurance protection, institutional development, insurance payments.
24.03.2024
 WAYS TO IMPROVE THE ECONOMIC EFFICIENCY OF FISH FARMING
WAYS TO IMPROVE THE ECONOMIC EFFICIENCY OF FISH FARMING
I.Yunusov – PhD, “Tashkent Institute of Irrigation and Agricultural Mechanization Engineers” National Research
University
Abstract: The article substantiates the objective need for the development of the fish farming industry, summarizes its features into a single system, develops recommendations for improving the system of indicators of the economic efficiency of fish farming, reveals the relationship of factors affecting the development of the industry, reveals significant aspects of foreign experience in the development of the industry. In particular, the ongoing reforms in the fish farming industry and trends in change, the state were analyzed, recommendations were developed on the basis of norms that provide for saving resources, reducing the cost of material, technical and labor resources necessary for growing fish.
Keywords: fisheries, aquaculture, efficiency of fisheries enterprises, production of fish products, state support for fisheries
24.03.2024
 THREATS ON THE WAY TO SPIRITUAL IMPROVEMENT AND WAYS TO ELIMINATE THEM
THREATS ON THE WAY TO SPIRITUAL IMPROVEMENT AND WAYS TO ELIMINATE THEM
F.Husnitdin Fakhriddin o’g’li, PhD student of “Tashkent Institute of Irrigation and Agricultural Mechanization
Engineers” National Research University
Abstract: This article shows the importance of the state youth policy pursued in our country today, as well as the importance of the original spiritual values formed by our ancestors. For the future of our independent state, we need people with high spirituality and harmonious development. The article analyzes the upbringing of young people and the factors affecting them at a time when threats and dangers to national identity and spiritual values are growing.
Keywords: Values, morality, spirituality, information crisis, patriotism, democracy
24.03.2024
 IMPORTANCE OF BEEKEEPING IN THE COUNTRY'S ECONOMY
IMPORTANCE OF BEEKEEPING IN THE COUNTRY'S ECONOMY
Sh.Hoshimova – Researcher of “Tashkent Institute of Irrigation and Agricultural Mechanization Engineers” National
Research University
Abstract: The sustainable development of agriculture and the improvement of food supply to the population is associated with solving the problem of increasing the efficiency of agricultural production in a country, industry, region, enterprise. An integral part of it is the development of the beekeeping industry, which is of independent importance in terms of identifying reserves for increasing the volume of production of its products and substantiating ways for a more rational use of bees in various fields of human activity.
Honey production in Uzbekistan is one of the priority areas of authentic agricultural products and can take a leading position in the world market.
Keywords: honey production, rational use of bees, beekeeping, pollination, forestry and climate regulation, ecosystems.
24.03.2024
 PROSPECTS FOR THE DEVELOPMENT OF CITRUS FARMING IN UZBEKISTAN
PROSPECTS FOR THE DEVELOPMENT OF CITRUS FARMING IN UZBEKISTAN
U. Khabibullaeva - PhD student of “Tashkent Institute of Irrigation and Agricultural Mechanization Engineers”
National Research University
Abstract: Fruit growing as a branch of agricultural production deals with the cultivation of perennial tree fruit species. The main
purpose of this industry is the production of fruits and berries, which are the food of the population and raw materials for the processing
industry. Citrus fruits are consumed fresh, they are distinguished by high palatability and have healing properties. They include useful
for the human body, sugars, acids, mineral salts, vitamins, proteins and essential oils. Among subtropical crops, oranges, lemons,
tangerines occupy an important place in terms of nutritional value and dietary value.
Keywords: citrus growing, subtropical crops, citrus farming, nutritional value, horticulture, greenhouses, resource-saving technologies.
23.03.2024
 ELECTROTECHNOLOGICAL METHODS OF DISINFECTION OF UNDERGROUND DRINKING WATER
ELECTROTECHNOLOGICAL METHODS OF DISINFECTION OF UNDERGROUND DRINKING WATER
The article studies the technology of disinfection of drinking water using water purification systems using ultraviolet radiation, operating on autonomous energy sources based on solar panels.
A.S. Berdishev - Doctor of Technical Sciences, Associate Professor,
N.M.Markayev - PhD, Senior Lecturer,
"Tashkent Institute of Irrigation and Agricultural Mechanization Engineers" National Research University
22.12.2023
 MEASURING AGRICULTURAL PRODUCTION DIVERSITY WITH THE REFERENCE SAMARKAND REGION
MEASURING AGRICULTURAL PRODUCTION DIVERSITY WITH THE REFERENCE SAMARKAND REGION
F.J. Saydullaeva, Ph.D. student
“Tashkent Institute of Irrigation and Agricultural Mechanization Engineers” National Research University
Abstract: This investigation is examined agricultural production diversification in a given period and space by a single quantitative
indicator. For the analyses conducted the survey in the Samarkand region, which areas produced the major agricultural products. The
results indicated that crop diversification was high at a value of 0.76 measured by Herfindahl Hirschman index in Samarkand region.
The level of livestock diversification is determined very low at value of 0.15. Government support for livestock diversification will serve
to increase rural households’ income and increase the consumption and production of high-calorie products.
Keywords: Crop diversification, Livestock diversification, Herfindahl Hirschman Index, Household, Samarkand region.
15.06.2023
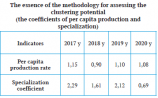 SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT OF WALNUT PRODUCTION ON THE BASIS OF INNOVATIVE-CLUSTER APPROACH
SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT OF WALNUT PRODUCTION ON THE BASIS OF INNOVATIVE-CLUSTER APPROACH
U.Sangirova – Associate professor, I.Yunusov – PhD, TIIAME National Research University
Abstract: The sustainable development of walnut growing is substantiated on the basis of a cluster approach, regional and sectoral partnership of walnut growing enterprises, food industry, scientific institutions, united by the program of innovative cluster development of the agro-industrial complex of the region. A set of program measures for the development of walnut growing for the period 2019-2021 is proposed for implementation at the regional level. as an innovative project.
Keywords: innovative cluster, walnut growing, walnut clusters, food industry, scientific institutions, climatic conditions, environmentally friendly products.
15.06.2023
 THEORETICAL AND PRACTICAL ASPECTS OF THE DIGITAL ECONOMY
THEORETICAL AND PRACTICAL ASPECTS OF THE DIGITAL ECONOMY
Sh.Mirzaev - Associate professor, "TIIAME" National Research University
Abstract: The article defines the theoretical foundations of the concept of digitalization of the economy and practical aspects of
digitalization for the development of water management. It is shown that Uzbekistan has significant scientific and resource potential
for the development of the digital economy, including modern water and agriculture. The purpose of the study is to analyze current
trends and prospects for the development of the digital economy in agriculture and water management, as well as to justify the
introduction of digital technologies in agribusiness and water management in the Republic of Uzbekistan.
Keywords: digitalization, agro-industrial complex, agriculture, neural network technologies, artificial intelligence, innovative
development, digital transformation, information and communication technologies.
15.06.2023
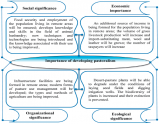 CIRCUMSTANCES NECESSITATING THE DEVELOPMENT OF PASTURE ANIMAL HUSBANDRY
CIRCUMSTANCES NECESSITATING THE DEVELOPMENT OF PASTURE ANIMAL HUSBANDRY
M.M.Yakhyaev – PhD student, “Tashkent Institute of Irrigation and Agricultural Mechanization Engineers” National
Research University
Abstract: In this article, the development of cattle breeding in our country goes into a deep history. This, in turn, gave a positive result
in the development of animal husbandry culture, experience, science, and in the first years of independence, special attention was paid to animal husbandry.
Keywords: Pasture, livestock, degradation, astrakhan fur, meat, breeding, wool, soil composition, temperature, vegetation composition and type of pasture, etc.
15.06.2023
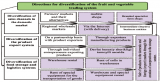 WAYS OF DEVELOPING A SYSTEM FOR DELIVERING PRODUCTS TO CONSUMERS IN INTENSIVE HORTICULTURE
WAYS OF DEVELOPING A SYSTEM FOR DELIVERING PRODUCTS TO CONSUMERS IN INTENSIVE HORTICULTURE
О.B.Sattorov – PhD, “TIIAME” National Research University
Abstract: Horticulture is one of the main spheres of agriculture. Fruits are widely used in a number of branches, such as: medical treatment, public health prevention (prophylaxis) and mainly in food production. But, only horticulture sphere cannot satisfy whole demand of people in fruit and vegetables.
Keywords: intensive gardening, efficiency, productivity, specialization, profitability
15.06.2023
 ECONOMIC CHARACTERISTICS OF THE PRODUCTION INFRASTRUCTURE
ECONOMIC CHARACTERISTICS OF THE PRODUCTION INFRASTRUCTURE
N.R.Kholmatova - PhD student, TIIAME National Research University
Abstract: Agriculture belongs to the life-supporting systems of society, forming its food resource, the state of which determines the national and economic security of the country. In addition, it acts as a basic industry for the development of rural areas, as it largely provides employment for the rural population, its standard of living, the vector of demographic processes and, ultimately, the reproduction of rural society. The agrarian economy is one of the priorities of the national economy, so as directly related to the state and development of the agri-food market, which is currently undergoing significant changes in the context of globalization. In addition, there are significant transformations in the agrarian sector under the influence of the characteristics of the post-industrial stage of development, associated with the aggravation of employment problems, the growth of qualification requirements, technological and infrastructural transformations, the deepening of contradictions between the general increase in the level of economic development and the traditional lag of the industry in comparison with other areas.
Keywords: production infrastructure, reproduction, management activities, food resource, agro-industrial complex, financial market.
15.06.2023
 EFFECTS OF PASTURE LIVESTOCK ON AGRICULTURAL LAND (ON THE EXAMPLE OF SAMARKAND REGION)
EFFECTS OF PASTURE LIVESTOCK ON AGRICULTURAL LAND (ON THE EXAMPLE OF SAMARKAND REGION)
Namozov Jurabek Abduazizovich - Associate Professor of Chirchik state pedagogical institute, doctor of philosophy (PhD) of Geographical Sciences. E-mail: jurabek.n.a@gmail.com
Rajabov Furkat Turakulovich – Head of the department of Chirchik state pedagogical institute, doctor of philosophy (PhD) of Geographical Sciences. f.rajabov@cspi.uz
Abstract: The article provides information about the changes in the agricultural lands of Samarkand region as a result of anthropogenic impacts and their consequences. The pastoral livestock state in the region, the number of cattle per 1 hectare of land and its impact degree are given in areas.
15.06.2023
 DEVELOPMENT OF AN EFFECTIVE SALES SYSTEM OF NUTS IN THE DOMESTIC AND FOREIGN MARKET
DEVELOPMENT OF AN EFFECTIVE SALES SYSTEM OF NUTS IN THE DOMESTIC AND FOREIGN MARKET
U.Sadullaev - Researcher at the International Center for Strategic Development and Research in Food and Agriculture,
PhD
Abstract: In this article, the object of the introduction of an effective system of growing and selling nuts in the country, the circumstances of its development, the factors affecting it have been investigated and proposals on improving the system of growing and selling nuts have been developed.
Keywords: nuts, sales, marketing, growing volume, private marketing centers, factors, necessity.
15.06.2023
 THE NEED TO DEVELOP DIGITALIZATION OF AGRICULTURE IN TERMS OF PANDEMY
THE NEED TO DEVELOP DIGITALIZATION OF AGRICULTURE IN TERMS OF PANDEMY
Sh.M.Murodov – PhD, Associate Professor, TIIAME National Research University
Abstract: This article highlights the main directions of development, implementation and the main problems of digitalization
of agriculture in the countries of the world, in particular, agriculture of the Republic of Uzbekistan in the modern conditions of the
spread of Coronavirus and self-isolation. In addition, current data and a comparative analysis of digital technologies introduced into
the agricultural sector are provided. Some suggestions were made for the development and implementation of digital technologies in
the agricultural sector.
Keywords: digitalization, agro-industrial complex, agriculture, neural network technologies, artificial intelligence, innovative
development, productivity
15.06.2023
 ECONOMIC EFFICIENCY OF HYDROPONIC FEED PRODUCTION FOR LIVESTOCK COMPLEXES
ECONOMIC EFFICIENCY OF HYDROPONIC FEED PRODUCTION FOR LIVESTOCK COMPLEXES
U.Sadullaev - PhD, Researcher at the International Center for Strategic Development and Research in Food and
Agriculture.
Abstract: This article provides a scientific basis for the need for hydroponic feed production for livestock complexes, its advantages, cost-effectiveness indicators and ways to encourage hydroponic feed production.
Keywords: livestock complexes, feed, hydroponics, cost-effectiveness, astrakhan cluster.
15.06.2023
 IMPROVEMENT OF THE CRITERIA AND METHODS FOR DETERMINING THE AMOUNT OF FINES USED FOR THE PURPOSE OTHER THAN THE DESIGNATION OF IRRIGATED LANDS IN AGRICULTURE
IMPROVEMENT OF THE CRITERIA AND METHODS FOR DETERMINING THE AMOUNT OF FINES USED FOR THE PURPOSE OTHER THAN THE DESIGNATION OF IRRIGATED LANDS IN AGRICULTURE
B.F.Sultanov - DSc, Professor, U.B.Mukhtarov - PhD, Senior lecturer
“Tashkent Institute of Irrigation and Agricultural Mechanization Engineers” National Research University
Abstract
The article conducts a study to determine the amount of fines for illegal use of irrigated agricultural land, i.e. for the use of irrigated lands for other purposes, for the protection, conservation of irrigated lands and preventing their use for other purposes.
Key words: agricultural land, irrigated land, fines, quality indicator, land violations, standard crop yield, current assessment, profit margin, agricultural products, average annual price.
15.06.2023
 THE USE OF ELECTRICAL METHODS FOR GROWING SWEET PEPPER SEEDLINGS T.M. Bayzakov, Sh.Yusupov, Tashkent Institute of Irrigation and Agricultural Mechanization Engineers F.F. Rasulov, B.A. Karimov, Scientific Research Institute of Vegetables, Melons and Potat
THE USE OF ELECTRICAL METHODS FOR GROWING SWEET PEPPER SEEDLINGS T.M. Bayzakov, Sh.Yusupov, Tashkent Institute of Irrigation and Agricultural Mechanization Engineers F.F. Rasulov, B.A. Karimov, Scientific Research Institute of Vegetables, Melons and Potat
With the development of new innovative technologies, it is necessary to study the operating conditions of energy
sources that can be used by consumers, their period of operation, the structure of which is in-depth. Extensive measures are
being taken to reduce labor and energy consumption in agricultural production, save resources, grow crops on the basis of
advanced technologies and develop high-efficiency environmentally friendly electrical devices. This article describes the role
of greenhouses in the cultivation of agricultural products and the use of electrical methods to increase the productivity of
their products, the components of electrical equipment and power sources involved in the process and the principles of their
operation.
Key words: Sweet pepper seedlings, lighting fixtures, quartz lamps, ultraviolet rays, Phyto lamps, greenhouse, land, food.
21.12.2021
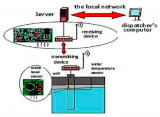 DEVELOPMENT OF AN AUTOMATED SYSTEM FOR MONITORING THE CURRENT STATE OF GROUNDWATER Sh.R. Ubaydullaeva – c.t.s., associate professor, A.M. Nigmatov - assistant Tashkent Institute of Irrigation and Agricultural Mechanization Engineers
DEVELOPMENT OF AN AUTOMATED SYSTEM FOR MONITORING THE CURRENT STATE OF GROUNDWATER Sh.R. Ubaydullaeva – c.t.s., associate professor, A.M. Nigmatov - assistant Tashkent Institute of Irrigation and Agricultural Mechanization Engineers
The article discusses the issues of control, accounting for the rational use of groundwater and methods for measuring
the water level in the well. It is proposed to measure the water level using radio waves. This method can be used in difficult
conditions, in particular at high pressure, at high temperatures without direct contact with the measured object. The problems
of monitoring the groundwater level and analyzing the state of measurement are considered. Recommendations are given on
instrumentation for level control, the creation and implementation of an automated observation system and an integrated
analysis system using a remote data transmission module via GSM. A program for monitoring the water level in a well has
been developed on the Arduino platform. A functional and structural diagram of an automated system for monitoring the state
of groundwater has been developed and technical means of automation have been selected. The selected radio module type
MX-RM-5V (433MNz), which transmits information in real time. Certificate (patent) No. DGU 117 24 dated May 19, 2021 was
received for the development of the software "Groundwater level measurement method"
Key words: groundwater monitoring, radar level gauge, data transmission via GSM, spectral analysis.
21.12.2021


